Get 50% off your partner's consultation fee when you purchase a consultation.
Driving growth through partnerships
Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra, or tube that transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, becomes irritated and inflamed. The male urethra also receives sperm.
Most episodes of urethritis are caused by infection by bacteria that enter the urethra from the skin around the urethra's opening. Bacteria that commonly cause urethritis include:
Many bacteria that cause urethritis can be passed from one person to another through sexual contact. As a result, practicing safe sex is a critical preventative measure. The following suggestions can assist you in lowering your risk:

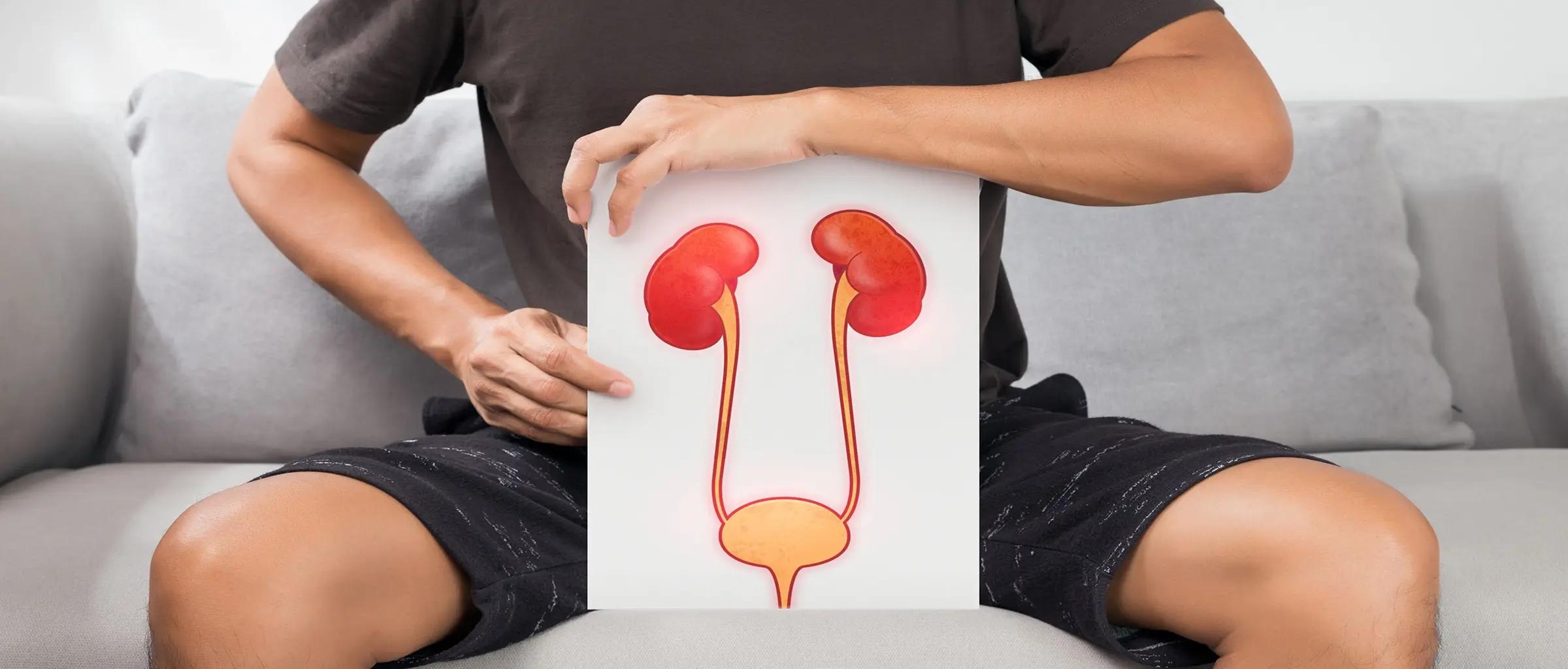
Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra, or tube that transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, becomes irritated and inflamed. The male urethra also receives sperm.
Urinary pain and an increased desire to pee are common symptoms of urethritis. The most common cause of urethritis is bacterial infection.
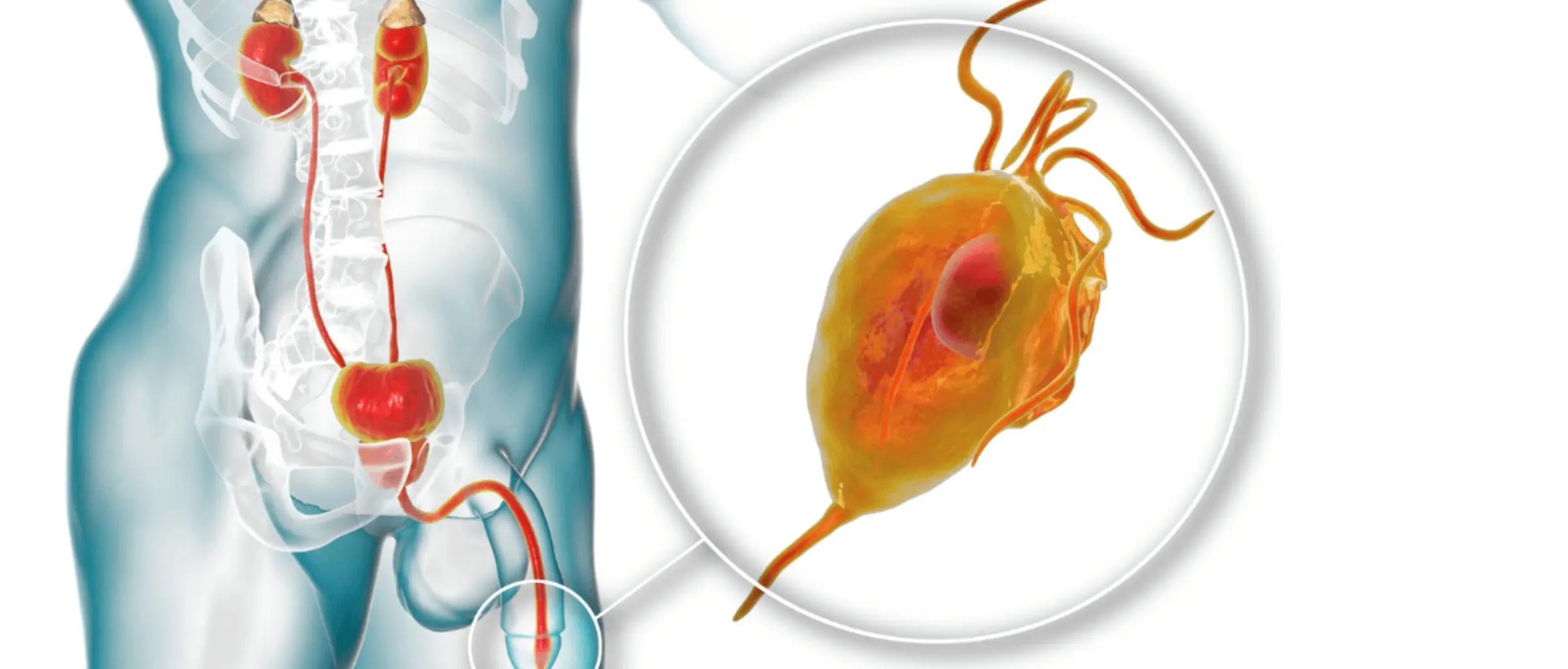
Most episodes of urethritis are caused by infection by bacteria that enter the urethra from the skin around the urethra's opening. Bacteria that commonly cause urethritis include:
The herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 and HSV-2) can also cause urethritis. Trichomonas is another cause of urethritis. It is a single-celled organism that is sexually transmitted.
Sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea and chlamydia are usually confined to the urethra. But they may extend into women's reproductive organs, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
In men, gonorrhea and chlamydia sometimes cause epididymitis, an infection of the epididymis, a tube on the outside of the testes. Both PID and epididymitis can lead to infertility.

Many bacteria that cause urethritis can be passed from one person to another through sexual contact. As a result, practicing safe sex is a critical preventative measure. The following suggestions can assist you in lowering your risk:
Males with urethritis may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
Some symptoms of urethritis in women include:
People who have urethritis may also not have any noticeable symptoms. This is especially true for women. In men, symptoms may not be apparent if the urethritis developed as a result of chlamydia or occasionally trichomoniasis infection.
For this reason, it’s important to undergo testing if you may have been infected with a sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Treatment for urethritis typically includes a course of either antibiotics or antiviral medication. Some
Starting from